This is Math Scholar blog. We are discussing some topic on Mathematics,Education , examination,Finance,Economics & Technology and other relevant topic. We are waiting for suggestion from you on which topics we can discuss for you.Thank you in advance feel free to comment.
Featured post
Math : Diffusion Equation or Heat Equation
Diffusion equation at finite rod, Semi-infinite rod and infinite rod have been discussed. Thank you. Feel free to comment.
1/29/2017
1/27/2017
Tech : Some Information about Payment Banks in India. What is Payment Banks and it's function?
Payments Banks:
This is a new model of bank in India incited by former RBI (Reserve bank of India ) governor Raghuram Rajan (2013-2016) in 2014.
These banks can accept a deposit upto ₹100,000 ($ 1500 around) per customer.
They can't issue loans and credit cards but can operate savings and current accounts. Also they can give services like ATM Cards, Debit Cards, Online Banking, Mobile Banking, UPI Banking ( Unified Payment Interface, This service launched by RBI), Aadhaar Banking (banking system use biometric authentication for payment no need any password or pin)
Requirement for Payments Banks :
The minimum capital requirement is ₹100 crore ($ 15m). Foreign share holding will be allowed in these banks as per rules of FDI ( foreign direct investment ) in the private banks in India.
These banks must use "Payments bank " term in their name. 70% of its deposited amount should be invest in the government bond ( India ) and 25% of its branches must be in the unbanked rural area.
Launched Payments banks :
Currently "Airtel Payments bank " has been launched on 15th January 2017, India Post has been launched on 30th january 2017 and "Paytm Payments bank" will be launched on the 1st week of February 2017.
RBI already given to these companies to launch Payments bank
1.India Post
2.Airtel M commerce
3. Airtel M commerce Services
4. Cholamandalam Distribution Services
5. Fino Pay Tech
6. National securities Depository
7. Reliance Industries
8. Sun pharmaceuticals
9. Paytm
10. Tech Mahindra
11. Vodafone M pesa etc.
Thank you. Come again. Feel free to comment.
Mathematics Syllabus for competitive exams and gate
Section 1: Linear Algebra
Finite dimensional vector spaces; Linear transformations and their matrix representations, rank; systems of linear equations, eigenvalues and eigenvectors, minimal polynomial, Cayley-Hamilton Theorem, diagonalization, Jordan-canonical form, Hermitian, SkewHermitian and unitary matrices; Finite dimensional inner product spaces, Gram-Schmidt orthonormalization process, self-adjoint operators, definite forms.
Section 2: Complex Analysis
Analytic functions, conformal mappings, bilinear transformations; complex integration: Cauchy’s integral theorem and formula; Liouville’s theorem, maximum modulus principle; Zeros and singularities; Taylor and Laurent’s series; residue theorem and applications for evaluating real integrals.
Analytic functions, conformal mappings, bilinear transformations; complex integration: Cauchy’s integral theorem and formula; Liouville’s theorem, maximum modulus principle; Zeros and singularities; Taylor and Laurent’s series; residue theorem and applications for evaluating real integrals.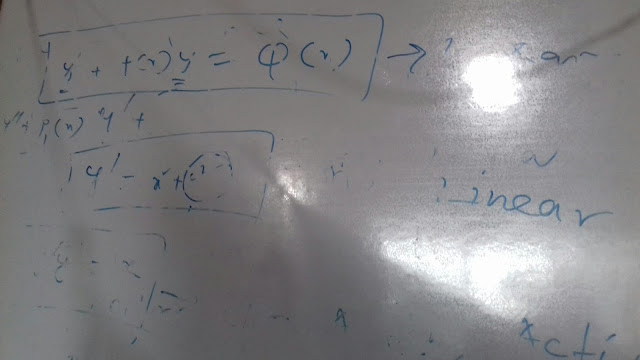
Section 3: Real Analysis
Sequences and series of functions, uniform convergence, power series, Fourier series, functions of several variables, maxima, minima; Riemann integration, multiple integrals, line, surface and volume integrals, theorems of Green, Stokes and Gauss; metric spaces, compactness, completeness, Weierstrass approximation theorem; Lebesgue measure, measurable functions; Lebesgue integral, Fatou’s lemma, dominated convergence theorem.
Sequences and series of functions, uniform convergence, power series, Fourier series, functions of several variables, maxima, minima; Riemann integration, multiple integrals, line, surface and volume integrals, theorems of Green, Stokes and Gauss; metric spaces, compactness, completeness, Weierstrass approximation theorem; Lebesgue measure, measurable functions; Lebesgue integral, Fatou’s lemma, dominated convergence theorem.
Section 4: Ordinary Differential Equations
First order ordinary differential equations, existence and uniqueness theorems for initial value problems, systems of linear first order ordinary differential equations, linear ordinary differential equations of higher order with constant coefficients; linear second order ordinary differential equations with variable coefficients; method of Laplace transforms for solving ordinary differential equations, series solutions (power series, Frobenius method); Legendre and Bessel functions and their orthogonal properties.
Section 5: Algebra
Groups, subgroups, normal subgroups, quotient groups and homomorphism theorems, automorphisms; cyclic groups and permutation groups, Sylow’s theorems and their applications; Rings, ideals, prime and maximal ideals, quotient rings, unique factorization domains, Principle ideal domains, Euclidean domains, polynomial rings and irreducibility criteria; Fields, finite fields, field extensions.
Section 6: Functional Analysis
Normed linear spaces, Banach spaces, Hahn-Banach extension theorem, open mapping and closed graph theorems, principle of uniform boundedness; Inner-product spaces, Hilbert spaces, orthonormal bases, Riesz representation theorem, bounded linear operators.
Section 7: Numerical Analysis Numerical solution of algebraic and transcendental equations: bisection, secant method, Newton-Raphson method, fixed point iteration; interpolation: error of polynomial interpolation, Lagrange, Newton interpolations; numerical differentiation; numerical integration: Trapezoidal and Simpson rules; numerical solution of systems of linear equations: direct methods (Gauss elimination, LU decomposition); iterative methods :Jacobi and Gauss-Seidel); numerical solution of ordinary differential equations: initial value problems: Euler’s method, Runge-Kutta methods of order 2.
Section 8: Partial Differential Equations
Linear and quasilinear first order partial differential equations, method of characteristics; second order linear equations in two variables and their classification; Cauchy, Dirichlet and Neumann problems; solutions of Laplace, wave in two dimensional Cartesian coordinates, Interior and exterior Dirichlet problems in polar coordinates; Separation of variables method for solving wave and diffusion equations in one space variable; Fourier series and Fourier transform and Laplace transform methods of solutions for the above equations.
Section 9: Topology
Basic concepts of topology, bases, subbases, subspace topology, order topology, product topology, connectedness, compactness, countability and separation axioms, Urysohn’s Lemma.
Section 10: Probability and Statistics Probability space, conditional probability, Bayes theorem, independence, Random variables, joint and conditional distributions, standard probability distributions and their properties (Discrete uniform, Binomial, Poisson, Geometric, Negative binomial, Normal, Exponential, Gamma, Continuous uniform, Bivariate normal, Multinomial), expectation, conditional expectation, moments; Weak and strong law of large numbers, central limit theorem; Sampling distributions, UMVU estimators, maximum likelihood estimators; Interval estimation; Testing of hypotheses, standard parametric tests based on normal, , , distributions; Simple linear regression.
Section 11: Linear programming
Linear programming problem and its formulation, convex sets and their properties, graphical method, basic feasible solution, simplex method, big-M and two phase methods; infeasible and unbounded LPP’s, alternate optima; Dual problem and duality theorems, dual simplex method and its application in post optimality analysis; Balanced and unbalanced transportation problems, Vogel’s approximation method for solving transportation problems; Hungarian method for solving assignment problems.
Thank you. https://amathscholar.blogspot.in/
SPIRITUAL : SILENCE IS THE MOST POWERFUL WORD IN WORLD
What is the powerful things in the world ?
money? people? No.
#Silence as It has no boundary. So don't think about people or money just about your love and passion. People and money can't give you peace but you can give it to you. It is not matter what people say about you. It is matter what you say about yourself and think about yourself.
You see people are selling each other because other are doing so.
Do you want to be like that people then you can do what they are doing. But if you don't want that do what you think and like.
some people may have bound to do this thing but why should you come in this bound? why would you see world by the other people mirror but your own mirror. ... It isn't that physical work is so much effective but #Silence .
Do you have seen Silence sea? Do you know how dangerous is a silence sea? You can't judge anything by seen a silence sea. If your mind go to the silence position think what mind can do.Is anything impossible for this mind? Silence can can create infinite possibility in the mind. Silence is the more effective than anything in the leaving creature.
What is the difference between men and other animals? Nothing but Silence. For this men are unstoppable.
Thank you. Come again. Please feel free to comment.
Spritual: Some times I become Thoughtless
Sometimes I become thoughtless and speechless, ask myself what do you want? My mind says don't know. Everything is within me so I don't need anything. Then I ask why are you searching here and there? In reply it says that to increase the awareness that Everything is within me. So why are you frustrated and fear about your job or work? Your job and work can't give anything to you except you. So don't fear do what you want.
Don't greed about anything as you can't get anything. You get what you are. So do what you love and what you think. Never mind what people say or think about you. You came in this world to search your love. For searching love don't afraid about physical pain of your body. In the physical pain of your body you will have your freedom and freedom is the ultimate goal of your life. Anything isn't matter to you expect freedom. In love there may be physical pain but don't give up your love. In the World you come here to search your love. See everything but choose what you love. Think about the people whom love you most. Do the work what you love.
Don't fear to lose. You are doing what you love. Don't think about result of the work as you are doing what you love.
Thank you. Please feel free to comment.
1/26/2017
Tech : BHIM App lunched by Narendra Modi, Best UPI App Review
1 #BHiM app is one the best upi app. It also very fast and transaction time is less than one sec. 9/10
Lotza is also very fast app also another feature of this app you can use many upi address and many account at a time. 9/10
3 Sbi pay this app is very very slow. If you wrongly enter your mobile number you can't change it by again uninstaling it.
3/10
3/10
4 Axis pay this is axis bank upi app. this app is also not so bad. Some people are facing problem that scan option is not working on their phone. This is not as so fast as first two app. 6/10
5 PhonePe this upi app is also good but one main concern is that you can't transfer your money from phonepe to another upi app. Transaction failure rate is very much. 8/10.
6 other upi app are #pockets and hdfc upi etc . they also good
.
Thank you. Come again. Please feel free to comment.
1/25/2017
Math : Csir Ugc Net syllabus for Mathematics
CSIR-UGC National Eligibility Test (NET) for Junior Research Fellowship and Lecturer-ship COMMON SYLLABUS FOR PART ‘B’ AND ‘C’ MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES
UNIT – 1
Analysis: Elementary set theory, finite, countable and uncountable sets, Real number system as a complete ordered field, Archimedean property, supremum, infimum. Sequences and series, convergence, limsup, liminf. Bolzano Weierstrass theorem, Heine Borel theorem. Continuity, uniform continuity, differentiability, mean value theorem. Sequences and series of functions, uniform convergence. Riemann sums and Riemann integral, Improper Integrals. Monotonic functions, types of discontinuity, functions of bounded variation, Lebesgue measure, Lebesgue integral. Functions of several variables, directional derivative, partial derivative, derivative as a linear transformation, inverse and implicit function theorems. Metric spaces, compactness, connectedness. Normed linear Spaces. Spaces of continuous functions as examples.
Linear Algebra: Vector spaces, subspaces, linear dependence, basis, dimension, algebra of linear transformations. Algebra of matrices, rank and determinant of matrices, linear equations. Eigenvalues and eigenvectors, Cayley-Hamilton theorem. Matrix representation of linear transformations. Change of basis, canonical forms, diagonal forms, triangular forms, Jordan forms. Inner product spaces, orthonormal basis. Quadratic forms, reduction and classification of quadratic forms
UNIT – 2
Complex Analysis: Algebra of complex numbers, the complex plane, polynomials, power series, transcendental functions such as exponential, trigonometric and hyperbolic functions. Analytic functions, Cauchy-Riemann equations. Contour integral, Cauchy’s theorem, Cauchy’s integral formula, Liouville’s theorem, Maximum modulus principle, Schwarz lemma, Open mapping theorem. Taylor series, Laurent series, calculus of residues. Conformal mappings, Mobius transformations.
Algebra: Permutations, combinations, pigeon-hole principle, inclusion-exclusion principle, derangements. Fundamental theorem of arithmetic, divisibility in Z, congruences, Chinese Remainder Theorem, Euler’s Ø- function, primitive roots. Groups, subgroups, normal subgroups, quotient groups, homomorphisms, cyclic groups, permutation groups, Cayley’s theorem, class equations, Sylow theorems. Rings, ideals, prime and maximal ideals, quotient rings, unique factorization domain, principal ideal domain, Euclidean domain. Polynomial rings and irreducibility criteria. Fields, finite fields, field extensions, Galois Theory.
Topology: basis, dense sets, subspace and product topology, separation axioms, connectedness and compactness.
UNIT – 3
Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs): Existence and uniqueness of solutions of initial value problems for first order ordinary differential equations, singular solutions of first order ODEs, system of first order ODEs. General theory of homogenous and non-homogeneous linear ODEs, variation of parameters, Sturm-Liouville boundary value problem, Green’s function.
Partial Differential Equations (PDEs): Lagrange and Charpit methods for solving first order PDEs, Cauchy problem for first order PDEs. Classification of second order PDEs, General solution of higher order PDEs with constant coefficients, Method of separation of variables for Laplace, Heat and Wave equations.
Numerical Analysis : Numerical solutions of algebraic equations, Method of iteration and Newton-Raphson method, Rate of convergence, Solution of systems of linear algebraic equations using Gauss elimination and Gauss-Seidel methods, Finite differences, Lagrange, Hermite and spline interpolation, Numerical differentiation and integration, Numerical solutions of ODEs using Picard, Euler, modified Euler and Runge-Kutta methods.
Calculus of Variations: Variation of a functional, Euler-Lagrange equation, Necessary and sufficient conditions for extrema. Variational methods for boundary value problems in ordinary and partial differential equations.
Linear Integral Equations: Linear integral equation of the first and second kind of Fredholm and Volterra type, Solutions with separable kernels. Characteristic numbers and eigenfunctions, resolvent kernel.
Classical Mechanics: Generalized coordinates, Lagrange’s equations, Hamilton’s canonical equations, Hamilton’s principle and principle of least action, Two-dimensional motion of rigid bodies, Euler’s dynamical equations for the motion of a rigid body about an axis, theory of small oscillations.
UNIT – 4
Descriptive statistics, exploratory data analysis Sample space, discrete probability, independent events, Bayes theorem. Random variables and distribution functions (univariate and multivariate); expectation and moments. Independent random variables, marginal and conditional distributions. Characteristic functions. Probability inequalities (Tchebyshef, Markov, Jensen). Modes of convergence, weak and strong laws of large numbers, Central Limit theorems (i.i.d. case). Markov chains with finite and countable state space, classification of states, limiting behaviour of n-step transition probabilities, stationary distribution, Poisson and birth-and-death processes. Standard discrete and continuous univariate distributions. sampling distributions, standard errors and asymptotic distributions, distribution of order statistics and range. Methods of estimation, properties of estimators, confidence intervals. Tests of hypotheses: most powerful and uniformly most powerful tests, likelihood ratio tests. Analysis of discrete data and chi-square test of goodness of fit. Large sample tests. Simple nonparametric tests for one and two sample problems, rank correlation and test for independence. Elementary Bayesian inference.
Gauss-Markov models, estimability of parameters, best linear unbiased estimators, confidence intervals, tests for linear hypotheses. Analysis of variance and covariance. Fixed, random and mixed effects models. Simple and multiple linear regression. Elementary regression diagnostics. Logistic regression. Multivariate normal distribution, Wishart distribution and their properties. Distribution of quadratic forms. Inference for parameters, partial and multiple correlation coefficients and related tests. Data reduction techniques: Principle component analysis, Discriminant analysis, Cluster analysis, Canonical correlation. Simple random sampling, stratified sampling and systematic sampling. Probability proportional to size sampling. Ratio and regression methods. Completely randomized designs, randomized block designs and Latin-square designs. Connectedness and orthogonality of block designs, BIBD. 2K factorial experiments: confounding and construction. Hazard function and failure rates, censoring and life testing, series and parallel systems.
Linear programming problem, simplex methods, duality. Elementary queuing and inventory models. Steady-state solutions of Markovian queuing models: M/M/1, M/M/1 with limited waiting space, M/M/C, M/M/C with limited waiting space, M/G/1.
All students are expected to answer questions from Unit I. Students in mathematics are expected to answer additional question from Unit II and III. Students with statistics are expected to answer additional question from Unit IV.
Thank you. Come again . Please feel free to comment.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
